Identify Characteristics That Describe a Grignard Reagent.
They are a subclass of the organomagnesium compounds. Does not dissolve a chemical sample well at low temperatures.

Grignard Reagent Formation Via C F Bond Activation A Centenary Perspective Chemical Communications Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 D1cc06753b
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area.

. X Cl Br I. Grignard reagent definition any of the group of reagents produced by the interaction of magnesium and an organic halide usually in the presence of an ether and having the general formula RMgX where R is an organic group and X is a halogen. While the starting organhalide is less reactive because it doesnt have a partial positive compound.
Alcohol we will react our Grignard reagent with a ketone more specifically benzophenone. Not yet answered Points possible. The preparation of a Grignard reagent.
The reaction with formaldehyde leads to a primary alcohol. 100 34 ratings The correct answer 1large 2Crystals 3slowly Af. A grignard reagent is an extremely strong nucleophile and can behave like carbonyl compounds with electrophiles.
Grignard Reagents are also used in the following important reactions. A Grignard reagent has a very polar carbonmagnesium bond in which the carbon atom has a partial negative charge and the metal a partial positive charge. Grignard reagents are used synthetically to form new carboncarbon bonds.
The resulting ketone rapidly reacts with a second equivalent of Grignard reagent giving rise to the tertiary alkoxide. This is intensified by the electronegative halide which gives it even more positive character. Identify the techniques used in the work-up and characterization of benzoic acid.
Identify the characteristics of a good recrystallization solvent 1. R alkyl aryl alkenyl allyl group. The purpose of this experiment is to prepare a Grignard reagent by reacting with alkyl or aryl halide and to ultimately react the Grignard reagent with carbon dioxide in order to produce carboxylate.
When an amido group substituent is used instead of the alkyl substituent amido magnesium halides are. What is Grignard Reagent. The Grignard reagent is more active with the attached magnesium because now it can be used as a nucleophile and a base.
Grignard reagent acts as a strong nucleophile and base it will react with many compounds including water. Grignard reagents are made by adding the halogenoalkane to small bits of magnesium in a flask containing ethoxyethane commonly called diethyl ether or just ether. The anionic portion acts as a strong.
Identify characteristics that describe a Grignard reagent. Defining key concepts - ensure that you can accurately classify Grignard reagents. Dissolves a chemical sample well at high temperatures 2.
Grignard Reagent Reactivity Magnesium Mg is a Group II metal with very low electronegativity. 100 2 ratings Transcribed image text. A typical Grignard reagent might be CH 3 CH 2 MgBr.
The organomagnesium halides are known as Grignard reagents. The addition of an excess of a Grignard reagent to an ester or lactone. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high.
Green identify the total number of atoms in conjugation. A grignard forms a violet. Grignard reagent is the chemical compound which contain magnesium along with halogen and alkyl group.
We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. It do not contain carboxylic acid. The carbon of a carbonyl is electrophilic and even though the carbon is a secondary carbon atom because it is planar it is an excellent site for a nucleophilic attack.
A Grignard reagent can be considered as an ionic compound with a magnesium halide cation and an organic anion. Two typical examples are methylmagnesium chloride ClMgCH3 and phenylmagnesium bromide C6H5MgBr. The initial attack gives rise to a tetrahedral intermediate which collapses to give a ketone and bromomagnesium ethoxide.
This quiz and worksheet allow students to assess the following. Grignard reagents are strong nucleophiles and can form carbon-carbon bonds making them somewhat similar to organolithium reagents. 2 pts g A common byproduct of Grignard reagent formation highlighting that the mechanism is more complicated than often depicted is a combination of two Grignard reagents.
100 After a recrystallization a. You can titrate the Grignard reagent following the procedure of Watson and Eastham in J. The Grignard reagent is represented as R-Mg-X where.
Grignard Reagent Lab Report. The flask is fitted with a reflux condenser and the mixture is warmed over a water bath. It is important to.
Was this answer helpful. Grignard reagents are potent nucleophiles and react with electrophilic esters. Identify characteristics that describe a Grignard reagent.
The Grignard Reaction is the addition of an organomagnesium halide Grignard reagent to a ketone or aldehyde to form a tertiary or secondary alcohol respectively. - The quick numeric analysis used to characterize the product and assess the purity. Which one of the following nucleophiles shows the highest nucleophilicity toward methyl iodide in.
View the full answer. The formed carboxylate is then protonated with an acid to produce carboxylic acid that could be. Use the provided 1H-NMR spectrum to determine the byproduct of this Grignard reaction.
These are extremely important reagents developed by the French chemist Francois Auguste Victor Grignard who was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1912 in Chemistry for this work. A Grignard reagent or Grignard compound is a chemical compound with the generic formula RMgX where X is a halogen and R is an organic group normally an alkyl or aryl. Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area.
A Grignard reagent is prepared when an _____ reacts with _____ in the solvent _____ organohalide magnesium ether.
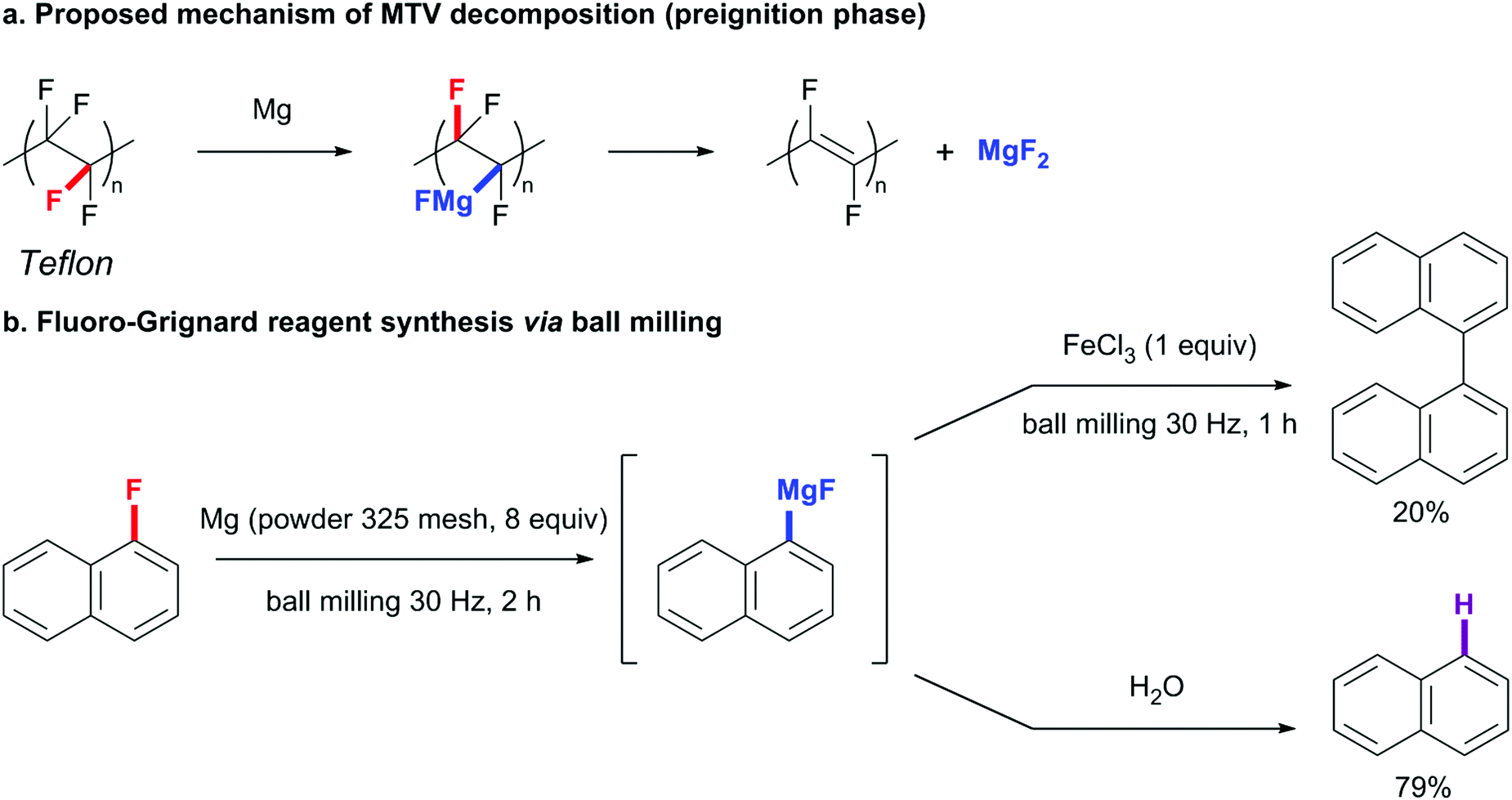
Grignard Reagent Formation Via C F Bond Activation A Centenary Perspective Chemical Communications Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 D1cc06753b
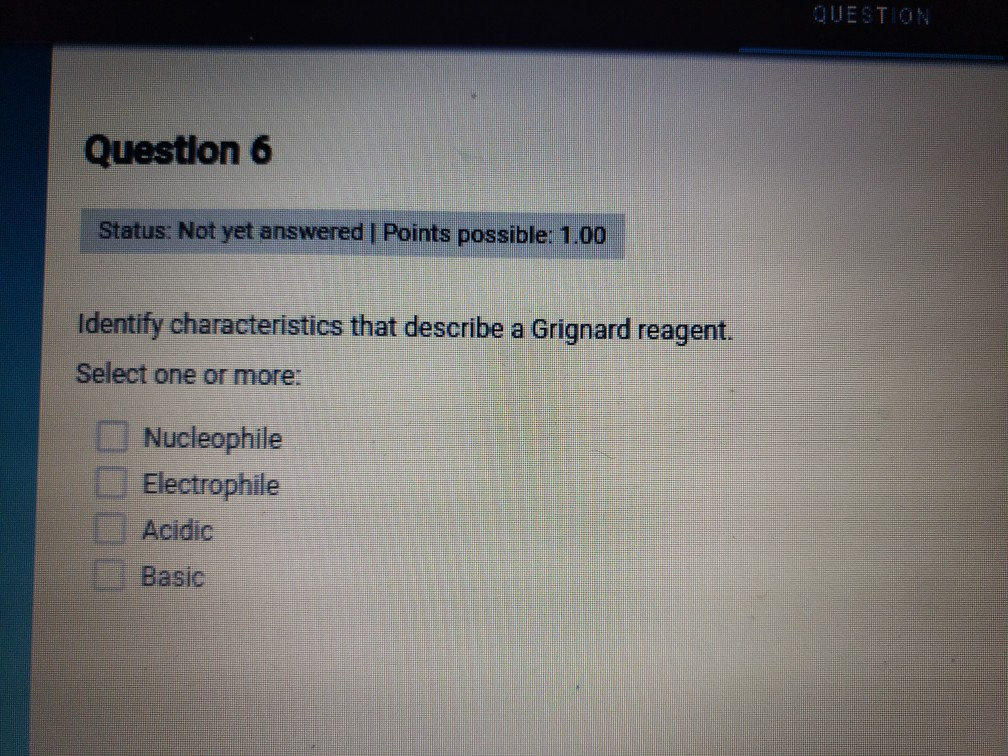
Solved Question 4 Status Not Yet Answered Points Chegg Com

Grignard Reagent Formation Via C F Bond Activation A Centenary Perspective Chemical Communications Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 D1cc06753b
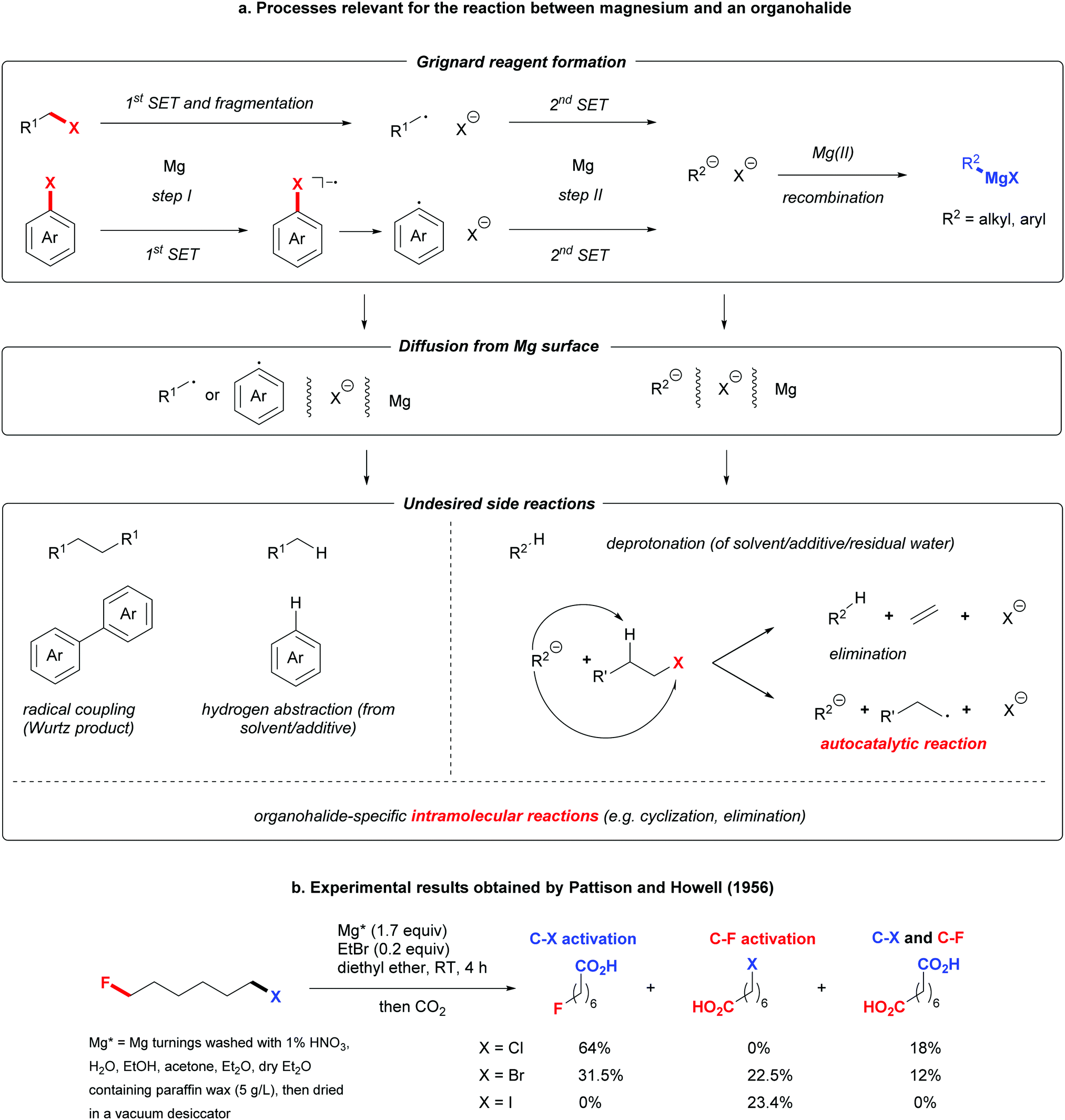
Grignard Reagent Formation Via C F Bond Activation A Centenary Perspective Chemical Communications Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 D1cc06753b

Grignard Reaction With Alcohol Ketone Aldehyde Overview Structures Uses Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Grignard Reagent Formation Via C F Bond Activation A Centenary Perspective Chemical Communications Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 D1cc06753b
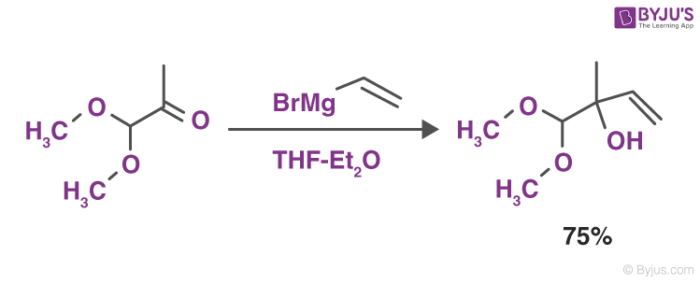
Grignard Reagents Preparation Reactions Organometallic Reagents
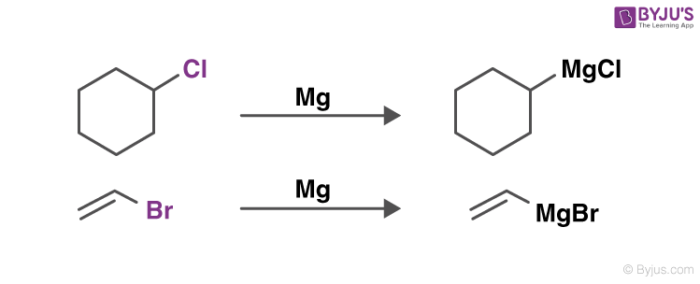
Grignard Reagents Preparation Reactions Organometallic Reagents

Organic Chemistry Summary Sheet Study Guides Chemistry Steps Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry Study Teaching Chemistry

Grignard Reaction With Alcohol Ketone Aldehyde Overview Structures Uses Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
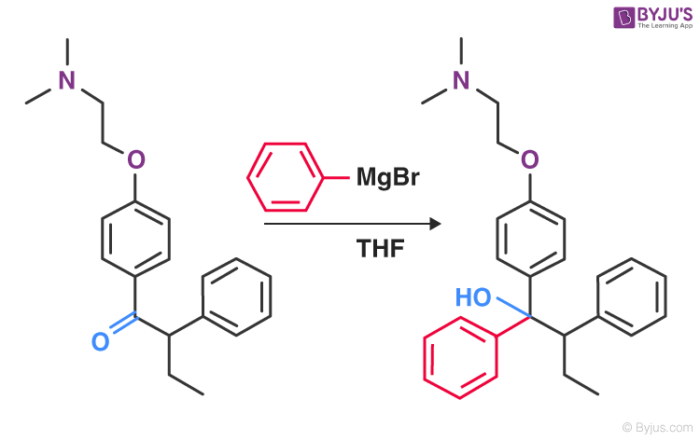
Grignard Reagents Preparation Reactions Organometallic Reagents

Solved Question 4 Status Not Yet Answered Points Chegg Com

Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry Reactions Teaching Chemistry

Grignard Reagent Formation Via C F Bond Activation A Centenary Perspective Chemical Communications Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 D1cc06753b
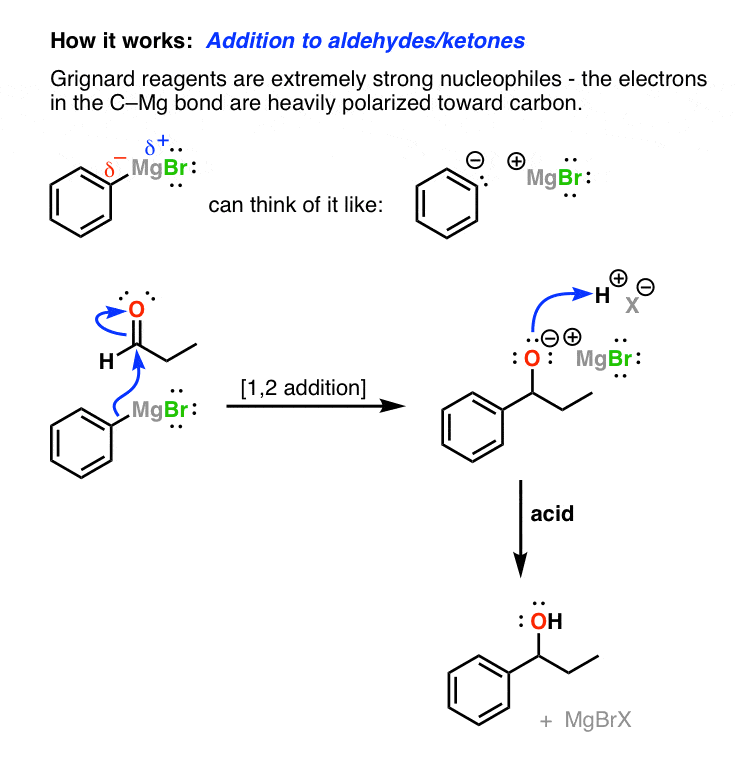
Grignard Reagents In Organic Chemistry Master Organic Chemistry

Grignard Reaction With Alcohol Ketone Aldehyde Overview Structures Uses Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Comments
Post a Comment